Computer Equipment Laboratory (Department of General Physics)
- About the laboratory
- Employees
- Teaching materials
About the laboratory
Head – Novosad I. S.
The Educational Laboratory of Computer Technology of the Department of General Physics is located in the premises of the Physics Faculty on the 19th Drahomanova street. The Laboratory includes the following units:
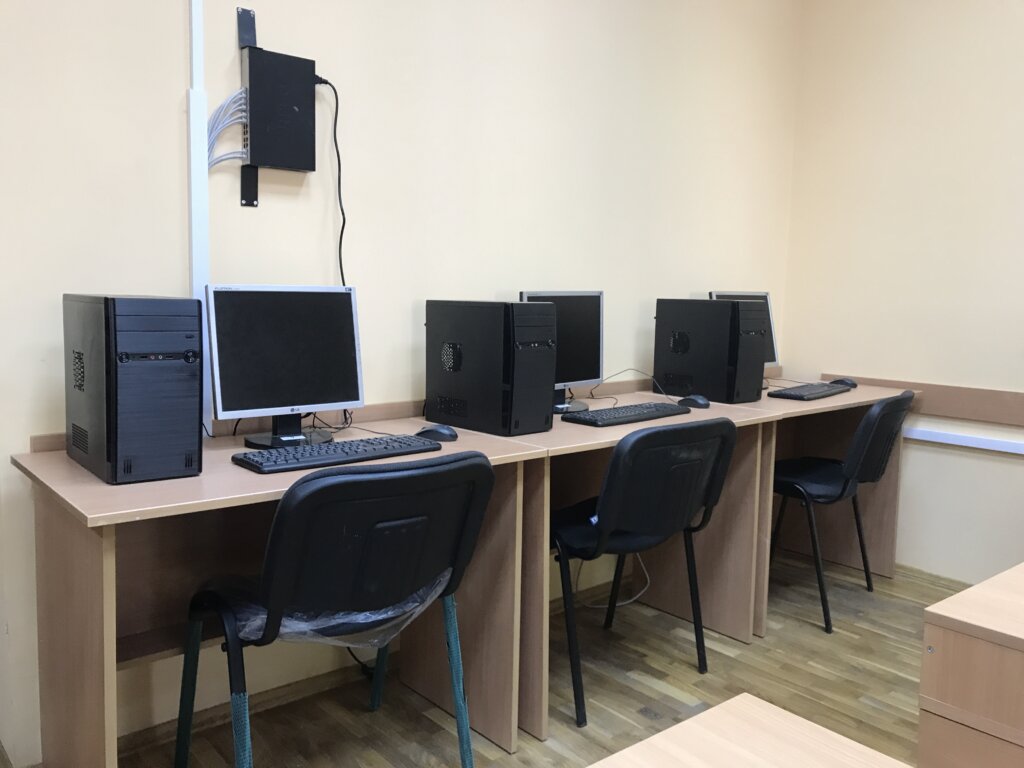
- Computer Class (room 202);
- Computer Physics Laboratory (room 301);
- Computerized Laboratory of Electricity and Magnetism (room 302);
- Computerized Laboratory of Functional electronics (room 303).
In the Laboratory of Electricity and Magnetism the laboratory works on the Physical Workshop (Electricity and Magnetism) (3rd sem., 2nd year), General Physical Workshop (Electricity and Magnetism) (2nd sem., 1st year), Fundamentals of Modern Electronics (6th sem., 3rd year), Fundamentals of Electronics (6th sem., 3rd year), Fundamentals of Radio Electronics (6th and 7th sem., 3rd and 4th year) for students of the following specialties::
- 104 Physics and Astronomy (Physics and Astrophysics, Computer Physics, Quantum Computers and Quantum Programming);
- 105 Applied Physics and Nanomaterials (Computer Technologies in Applied Physics, Nanophysics and Nanomaterials);
- 014.08 Secondary Education (Physics).
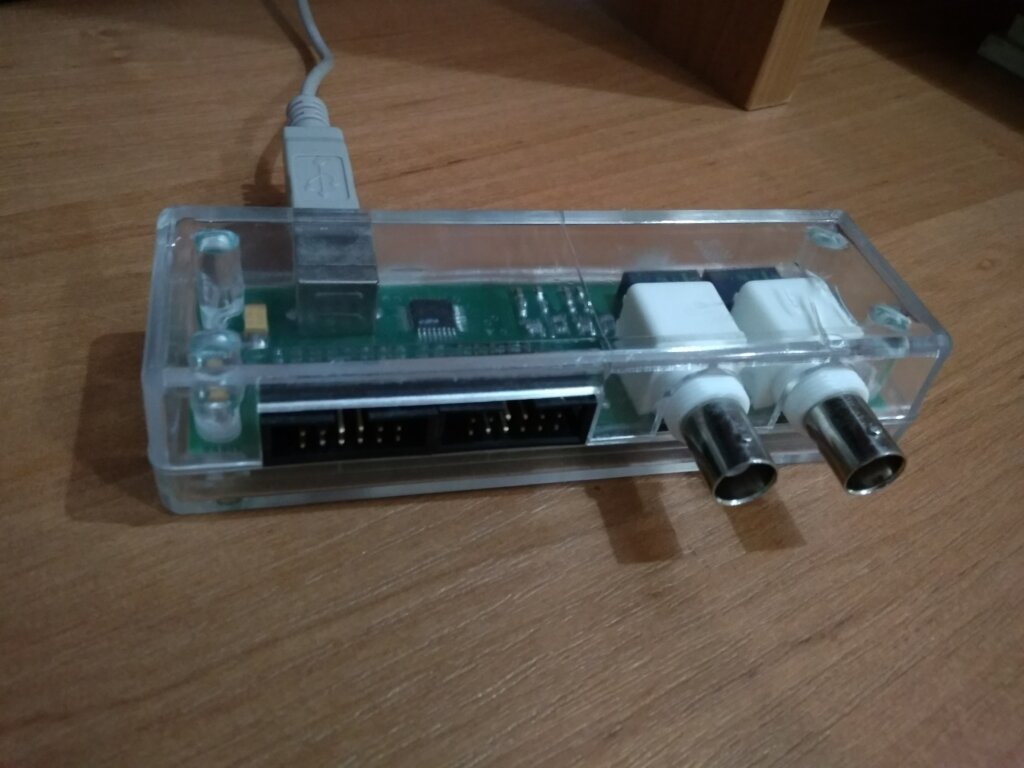
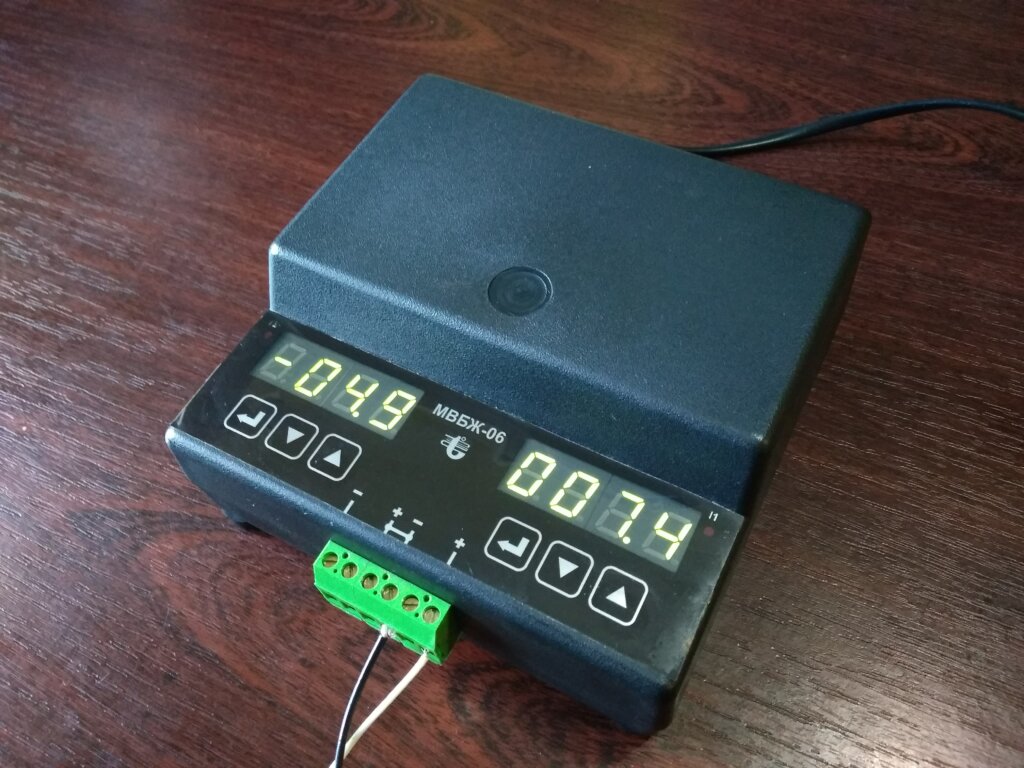
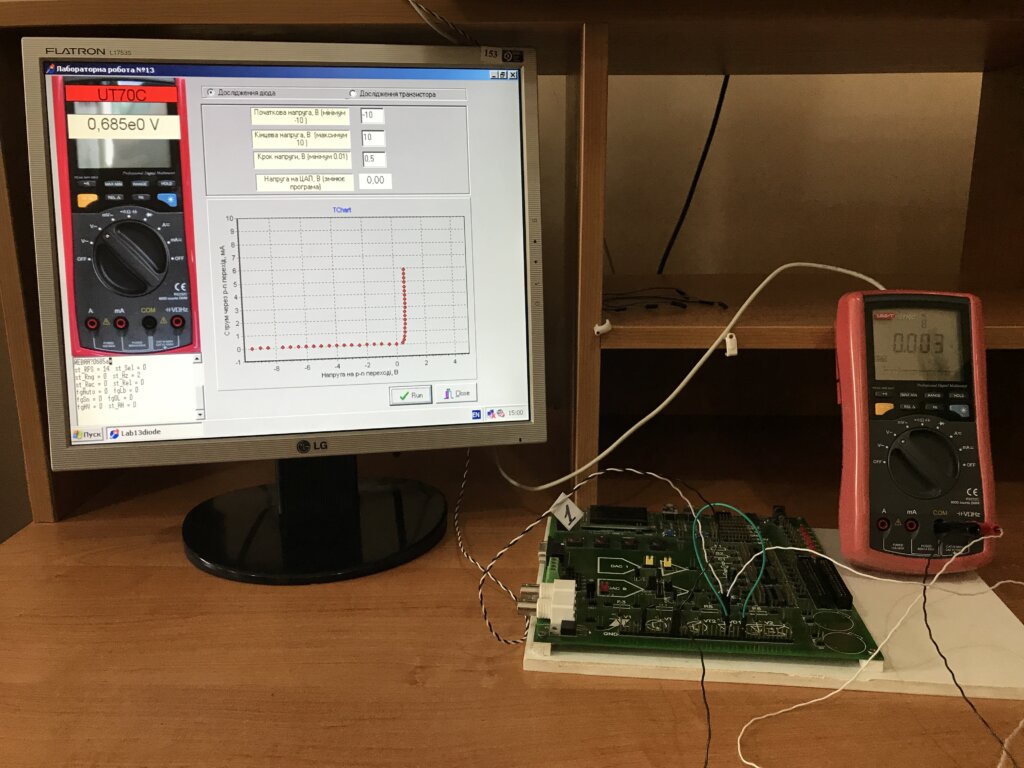
Devices and equipment: PC (Celeron), circuit boards, USB-oscilloscopes, digital multimeters (UT70C, АХ-18В), power supplies (MVBZh-06), in addition, DC power supplies (B5-43, B5-47, B5-49) are used for some laboratory works; a source of a direct current (B5-44A), a power supply (VIP-009, VIP-010), the stabilizer of tension of a direct current (P4105), the generator of signals of the special form (G6-28), the generator of signals low-frequency (G3-112/1), frequency meter (Ch3-54), pulse generator (G5-56), analog oscilloscopes (C1-68, C1-73, C1-93), universal monochromator (MUM), KAMAK system. The appearance of some laboratory devices is presented in Figs. 1-4.
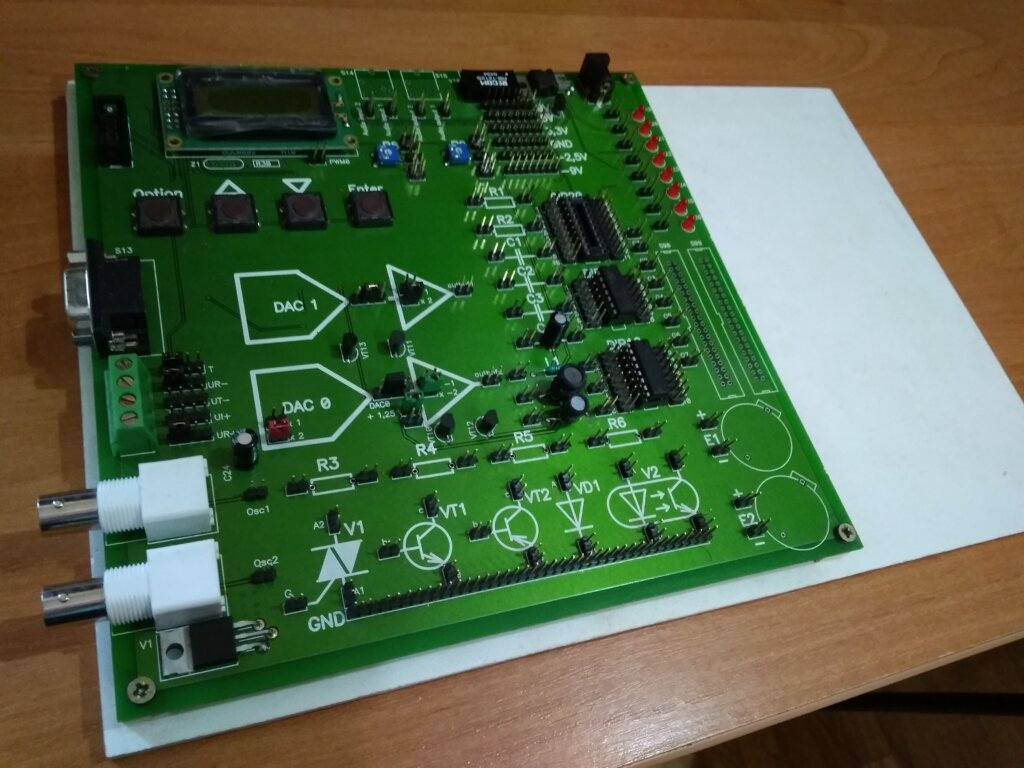

Fig.1. Layout of universal electronic board.
List of laboratory works of the Electricity and Magnetism discipline:
- Electrical measurements and measurement methods.
- Measurement of parameters of electric signals by means of the oscilloscope.
- Study of Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s rules.
- Study of the electrostatic field.
- Measurement of electrical properties of ferroelectrics.
- Determination of the horizontal component of the Earth’s magnetic field.
- Study of the Hall effect.
- Observation of magnetization processes of ferromagnetics.
- Study of the self-induction phenomenon.
- Establishment of dependence of resistance of metal and semiconductor on temperature.
- Determination of thermoelectric phenomena.
- Measurement of the characteristics of the vacuum diode and triode.
- Semiconductor diode and transistor.
- Study of alternating current circuits.
- Resonance phenomena in alternating current circuits.
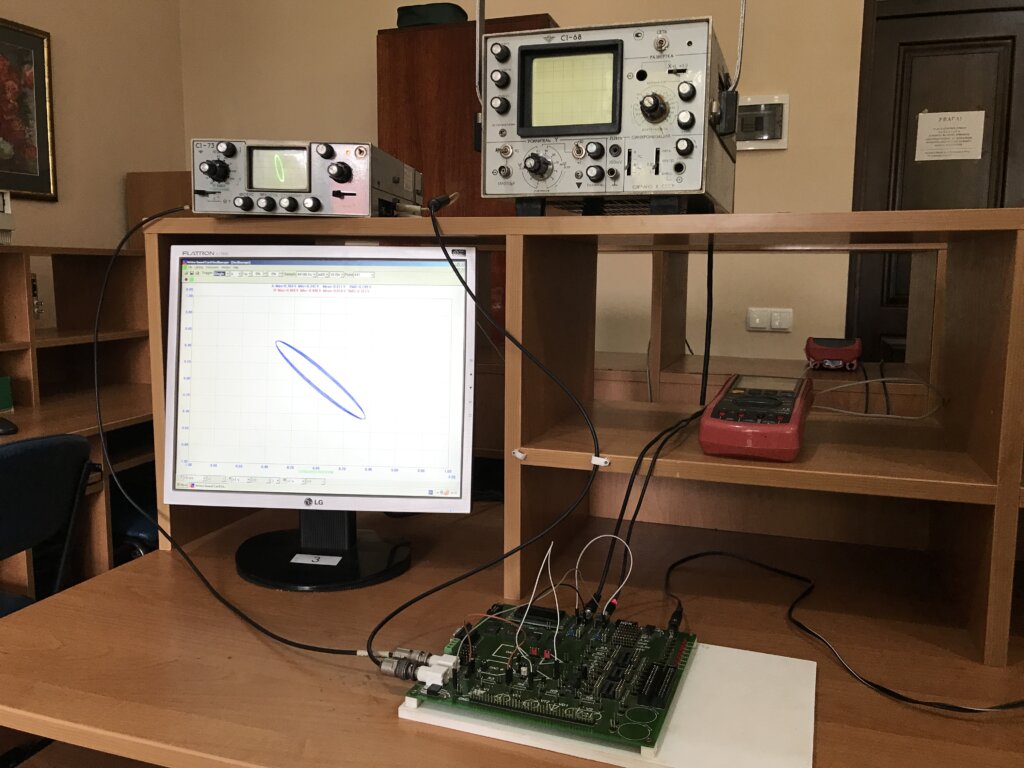
Fig. 5. Laboratory work No 2: “Measurement of parameters of electrical signals using an oscilloscope”
List of laboratory works on the subject
Fundamentals of Modern Electronics (Fundamentals of Electronics):
- Element base and devices of modern radio electronics.
- Construction of filters of electric signals from passive elements.
- Digital processing of radio signals.
- Study of field-effect transistors and measurement of their characteristics.
- Voltage amplifier on bipolar transistors.
- Study of operational amplifiers.
- Study of optoelectronic devices.
- Optocouplers as elements of galvanic isolation.
- Modeling of electrical circuits using the Electronics Workbench package.
- Working with LabView.
List of laboratory works on the
Fundamentals of Radio Electronics subject:
First semester:
- Element base and devices of modern radio electronics.
- Construction of filters of electric signals from passive elements.
- Digital processing of radio signals.
Second semester:
- The use of diodes and Zener diodes in power circuits.
- Voltage amplifier on bipolar transistors.
- Voltage repeater on bipolar transistors.
- Study of field-effect transistors and measurement of their characteristics.
- Study of operational amplifiers.
- Study of optoelectronic devices.
- Optocouplers – elements of galvanic isolation.
- Simulation of electrical circuits using the Electronics Workbench package.
- Working with LabView.
- Study of digital logic elements.
- Programming of microcontrollers for conversion of electric signals.
The Laboratory of Computer Physics provides laboratory works in the following disciplines for 4th year students and 1st year undergraduates of study in the specialty 105 Applied Physics and Nanomaterials:
- Sensors and transducers of physical quantities (7th semester);
- Applied Physics (Computer Measuring Systems) (7th semester);
- Physical basics of computer systems (undergraduates, 2th semester);
- Phase transitions in crystalline systems (undergraduates, 2th semester);
- Physics of dielectric crystals (8th semester).
In the Computerized Laboratory of Functional Electronics, students have opportunity to master skills of research work during the preparation of term papers and master’s theses.
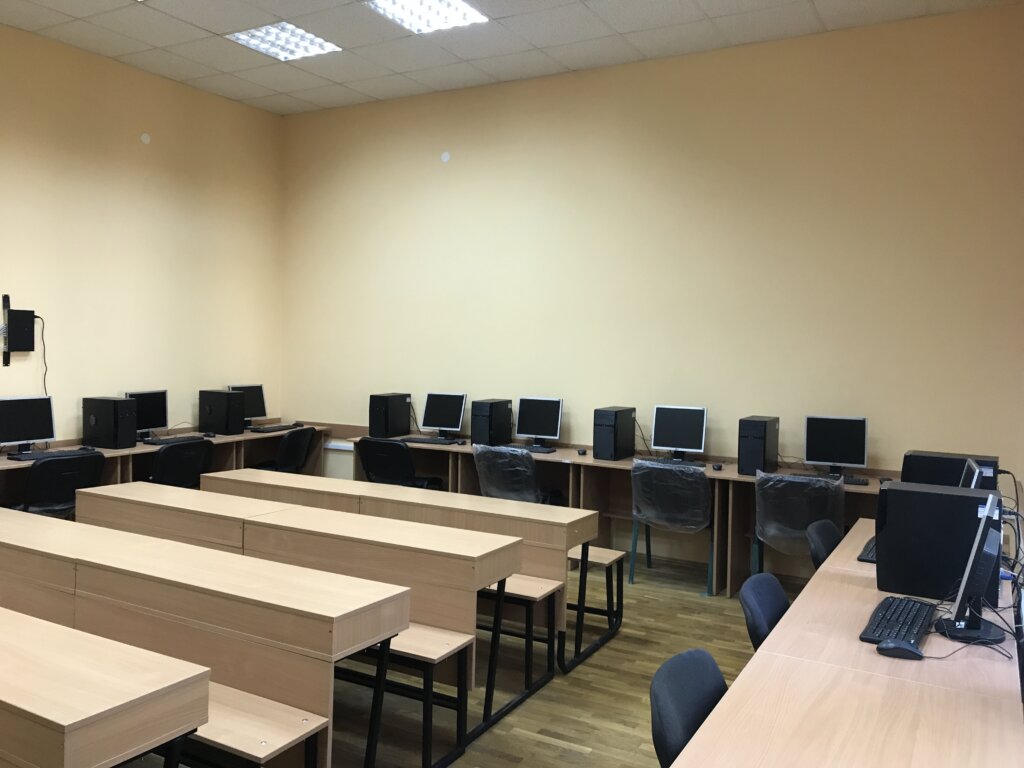
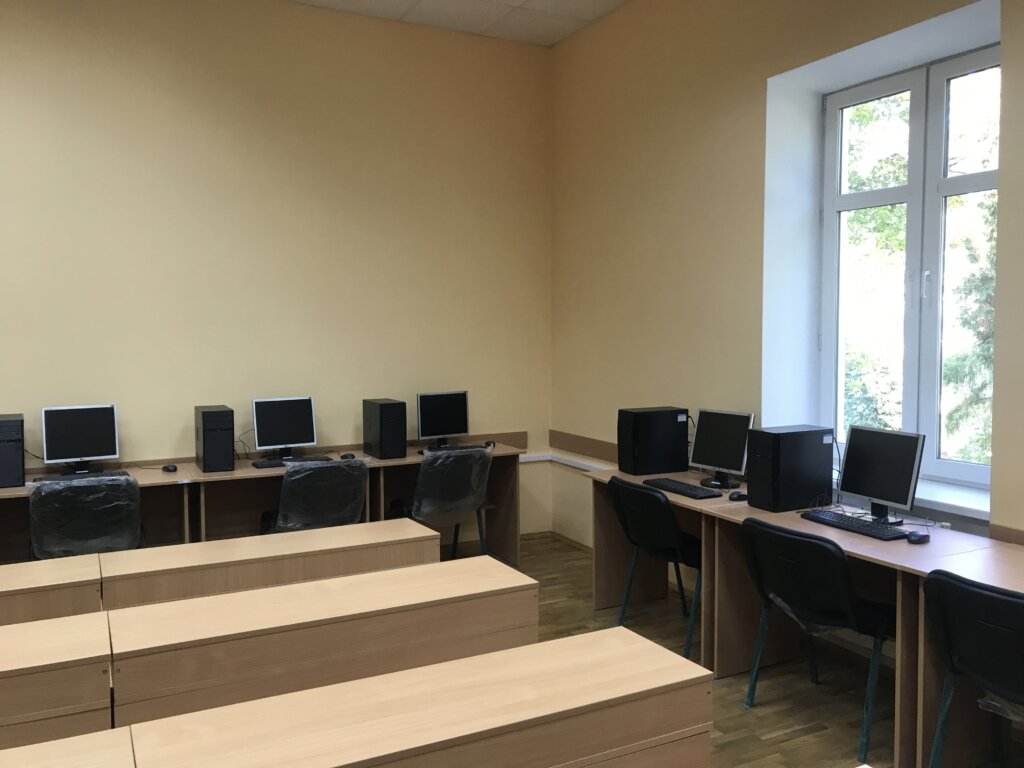
The computer class (11 PCs) conducts laboratory works in the following disciplines:
- Engineering computer graphics (105 Applied Physics and Nanomaterials; 3rd semester, 2nd year);
- Fundamentals of computer graphics (Discipline of free choice; 3rd semester, 2nd year);
- Analog and digital methods of image processing (105 Applied Physics and Nanomaterials; 5th semester, 2nd year);
- Methods of signal and image processing (104 Physics and Astronomy (Experimental Physics); undergraduates, 3rd semester, 2nd year);
- Computer modeling of physical processes (104 Physics and astronomy; 7th and 8th semesters, 4th year);
- Fundamentals of expert systems (105 Applied Physics and Nanomaterials; undergraduates, 1st semester, 1st year);
- Computer methods of modeling physical processes (105 Applied Physics and Nanomaterials; 8th semester, 4th year);
- Modeling of physical properties of materials (105 Applied Physics and Nanomaterials; 8th semester., 4th year);
- Digital signal processing (104 Physics and Astronomy, 105 Applied Physics and Nanomaterials, 014.08 Secondary education (Physics); 3rd semester, 2nd year).
The Computer Class offers programming and computer simulation classes (Fig. 9-11):
In addition, employees of the General Physics Department also closely cooperate with the Lviv Regional Small Academy of Sciences and contribute to the education of the future generation of qualified physicists. From September 2022 until now pupils are studying the course “Electricity and magnetism” in depth with great interest, passing laboratory work, where theoretical material is readily explained to them, and they have assistance in conducting an experiment and calculating the relevant quantities based on the obtained results.
In the process of learning, pupils performed 8 laboratory works under the guidance of assistant I. A. Pryshko:
- Electrical measurements and measurement methods;
- Study of Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s rules;
- Electrostatic field study;
- Study of the horizontal component of the intensity of the Earth’s magnetic field;
- Study of the Hall effect;
- Establishing the dependence of metal and semiconductor resistance on temperature;
- Study of thermoelectric phenomena;
- Determination of the specific resistance of a resistive wire by a technical method.
They also had the opportunity to listen to the lecture on “Electric current in different environments” (read by assistant I. A. Pryshko).
Employees
| Laboratory Chief ManagerIryna Novosad | Laboratory Chief Manager |
| Lead EngineerOksana Radkovska | Lead Engineer |
Teaching materials
- Вакарчук С. О. Фізика : підручник : [для вищ. навч. закл. (гриф МОН України)] / С. О. Вакарчук, Т. М. Демків, С. В. Мягкота. – Львів : ВЦ ЛНУ імені Івана Франка, 2010. – 458 с.
- Антоняк О. Т. Загальна фізика. Основи електрики і магнетизму : навч. посіб. : [для вищ. навч. закл.] / О. Т. Антоняк. – Львів : ВЦ ЛНУ імені Івана Франка, 2009. – 240 с.
- Шопа Я. І. Електрика та магнетизм. Лабораторний практикум : навч. посіб. : [для студ. фіз. ф-ту] / Я. І. Шопа, В. М. Лесівців. – Львів : ВЦ ЛНУ імені Івана Франка, 2007. – 106 с.
- Шопа Я. І. Основи радіоелектроніки. Лабораторний практикум : навч. посіб. : [для студ. фіз. ф-ту] / Я. І. Шопа. – Львів : ВЦ ЛНУ імені Івана Франка, 2008. – 116 с.
- Демків Т. М. Основи теорії похибок фізичних величин. Методичні матеріали для загального фізичного практикуму / Т. М. Демків, О. І. Конопельник, Я. І. Шопа. – Львів : ВЦ ЛНУ імені Івана Франка, 2008. – 40 с.
- Lab №10 “Establishment of dependence of resistance of metal and semiconductor on temperature” course “Electricity and Magnetism”.